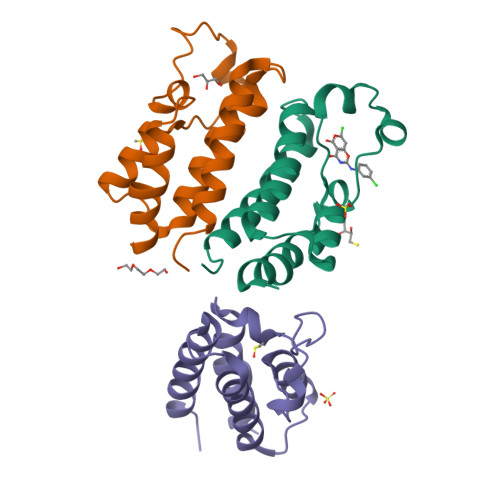
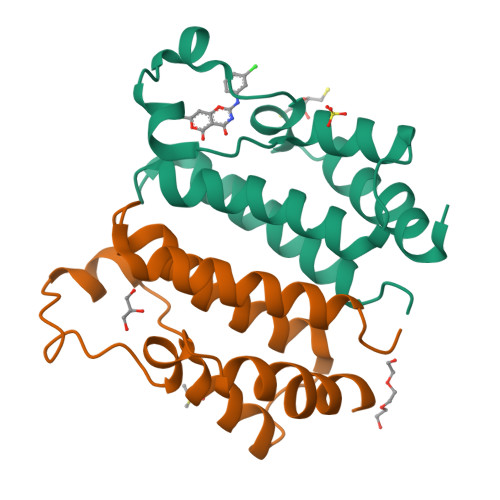
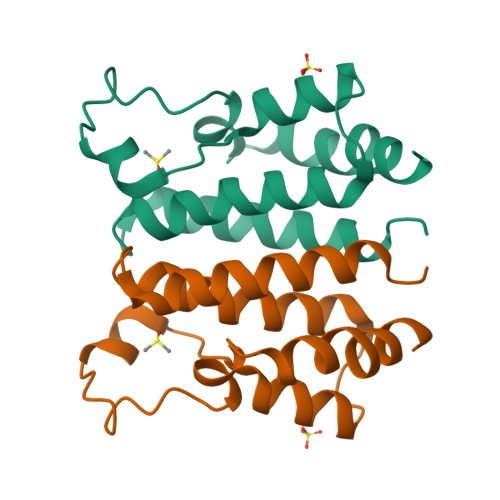
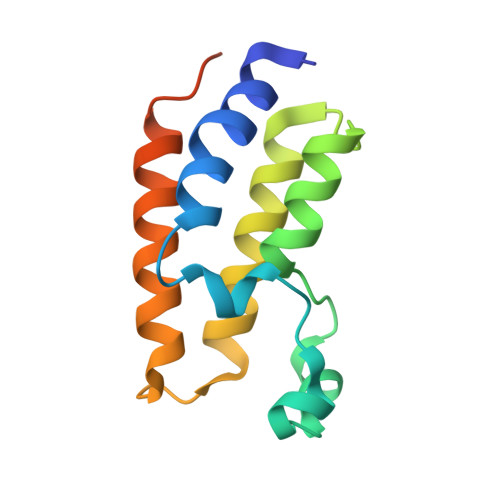
Novel pyrano 1,3 oxazine based ligand inhibits the epigenetic reader hBRD2 in glioblastoma.
Deshmukh, P., Mathur, S., Gangadharan, G., Krishnappa, G., Dalavaikodihalli Nanjaiah, N., Padmanabhan, B.(2020) Biochem J 477: 2263-2279
- PubMed: 32484211
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1042/BCJ20200339
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6JKE - PubMed Abstract:
Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most common primary brain malignancy, rarely amenable to treatment with a high recurrence rate. GBM are prone to develop resistance to the current repertoire of drugs, including the first-line chemotherapeutic agents with frequent recurrence, limiting therapeutic success. Recent clinical data has evidenced the BRD2 and BRD4 of the BET family proteins as the new druggable targets against GBM. In this relevance, we have discovered a compound (pyrano 1,3 oxazine derivative; NSC 328111; NS5) as an inhibitor of hBRD2 by the rational structure-based approach. The crystal structure of the complex, refined to 1.5 Å resolution, revealed that the NS5 ligand significantly binds to the N-terminal bromodomain (BD1) of BRD2 at the acetylated (Kac) histone binding site. The quantitative binding studies, by SPR and MST assay, indicate that NS5 binds to BD1 of BRD2 with a KD value of ∼1.3 µM. The cell-based assay, in the U87MG glioma cells, confirmed that the discovered compound NS5 significantly attenuated proliferation and migration. Furthermore, evaluation at the translational level established significant inhibition of BRD2 upon treatment with NS5. Hence, we propose that the novel lead compound NS5 has an inhibitory effect on BRD2 in glioblastoma.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Biophysics, National Institute of Mental Health and Neuro Sciences (NIMHANS), Hosur Road, Bangalore 560029, India.